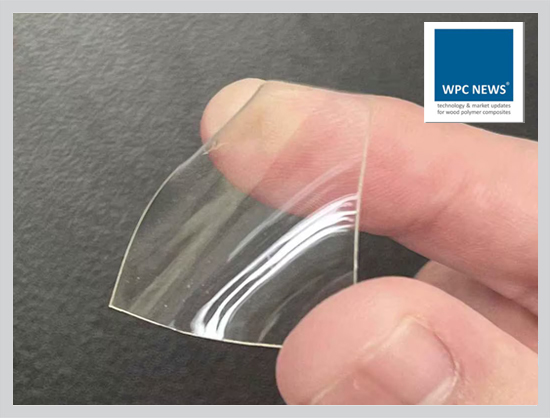
Product and industry
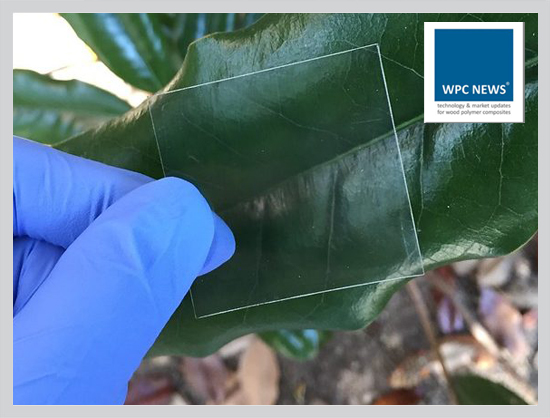
Transparent wood is a relatively new material. For the first time, it was created in 1992 by a German researcher Siegfried Fink. Back then he turned wood transparent to reveal its specific cavities for analytical purpose. In 2015-2016 researchers from Swedish KTH University and University of Maryland developed a method to remove colour and some chemicals from small wood samples and added polymers to make it transparent.

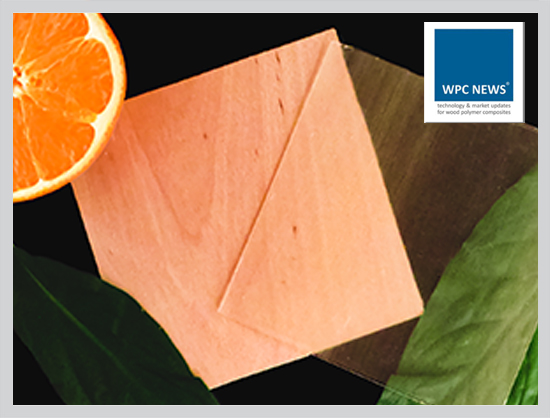
The production of transparent wood involves dissolving lignin and replacing it with another transparent material, followed by nano-level treatment and final treatment with a transparent polymer. Two structural variants exist: multilayer transparent wood and single-layer transparent wood, both having the same thickness but differing in physical and chemical properties. Multilayer transparent wood is considered superior due to its lighter weight, fewer internal cracks, better light transmittance, improved mechanical strength, and smoother interfaces.
Transparent wood finds practical applications in various industries. Common uses include windows and solar panels, where it ensures sunlight transmittance and effective thermal insulation. Engineers are exploring innovative applications such as touch-sensitive wooden dashboards in augmented reality.
Beyond construction and energy-related applications, transparent wood is making its way into diverse fields. In biomedical devices, automotive windshields, packaging, flexible electronics, and high-end sports equipment, transparent wood offers unique advantages. Its use extends to lightweight vehicles, thermally insulative wood, and paper for consumer electronics and batteries.
The versatile properties of transparent wood make it a material of interest for numerous industries, showcasing its potential to contribute to sustainable, high-performance solutions in various technological and manufacturing domains. As research and development in this field progress, the applications of transparent wood are likely to expand even further.
An attractive alternative to fossil fuel-derived materials
Transparent wood, initially developed as a replacement for window glass, has evolved into a recognized and sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-derived materials. Its biodegradable properties and minimal generation of toxic chemicals during production make it environmentally friendly. In comparison to glass, transparent wood exhibits resilience to stronger impacts, bending or splintering instead of shattering, as highlighted by the Building Designers Association of Australia.
Studies, such as those published in the Science of the Total Environment, underscore the significant potential of transparent wood in reducing carbon emissions and supporting low-carbon lifestyles. It is reported to be up to 10 million times more sustainable than polyethylene wood, presenting a compelling case for its adoption in various applications.
However, the widespread production of transparent wood carries the risk of contributing to deforestation. Balancing the environmental benefits of transparent wood with sustainable and responsible production practices is crucial to fully realize its potential as a green alternative to conventional materials. Efforts to address these challenges will be essential in ensuring the continued environmental benefits of transparent wood and mitigating any negative impacts on ecosystems.
Innovation and technological trends
Transparent wood offers significant efficiency advantages over traditional glass, being five times more efficient. This increased efficiency is attributed to reduced processing time and decreased chemical and energy consumption during production. When used as a replacement for glass glazing systems, transparent wood has the potential to reduce space conditioning energy consumption by 24.6% to 33.3% in medium and large office spaces.
Beyond its energy-efficient properties, transparent wood has the capability to store carbon, making it environmentally friendly. Its applications extend to heat storage, making it a popular choice in construction and air industries, including small aircraft.
Research efforts are ongoing to further enhance the properties of transparent wood. Focus areas include improving durability against water damage, clarity, strength, and exploring its potential as a bulletproof material. Additionally, researchers are investigating different tree species, scaling up production, industrializing the production process (including recycling possibilities and circular credentials), understanding the interaction between light and wood structure, and exploring advanced composite applications.
The demand for transparent wood, particularly in the production of optical materials, has seen a significant rise. As research continues to advance and commercialization efforts progress, transparent wood is likely to find even broader applications in various industries, contributing to sustainable and energy-efficient solutions.
Transparent wood market
The global transparent wood market is expected to experience steady growth, with a projected CAGR of 9.0% from 2022 to 2031, reaching a size of $208.1 million. Recent market trends include acquisitions, mergers, product launches, and expansion by key players. The construction segment currently holds the largest share, accounting for nearly one-third of the global transparent wood market, while the solar cell segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR of 9.4% from 2022 to 2031.
North America is anticipated to be the largest market, with Europe projected to register robust growth until 2031. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the fastest CAGR of 9.5%. Construction activities are on the rise in the U.S. and Canada, driven by abundant wood supply, the aesthetic appeal of wood, and its environmentally sound qualities. Renovation and rework activities contribute to the growing popularity of transparent wood worldwide, with consumers expressing strong demand for its energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness. In Asia, particularly in Japan and China, there is an increasing demand for wood products, and transparent wood is gaining attention. India is also undergoing a transition influenced by global furniture companies.
The outlook for the transparent wood market appears promising, with various regions and applications contributing to its growth. The market’s trajectory reflects the increasing interest in sustainable and innovative building materials.
Reference: https://biogateway.efi.int/transparent-wood/
European Forest Institute, Yliopistokatu 6B, 80100 Joensuu, Finland